

Our Work
What We Do
At CIDA, we collaborate closely with rural communities to co-create impactful, locally-driven solutions in livelihoods, health, education, and agriculture. We bridge traditional knowledge with appropriate technologies and lived experience to deliver practical, scalable, and sustainable development outcomes.
Our work is rooted in the principles of equity, inclusion, and sustainability—ensuring lasting impact without harm, and leaving no one behind.
From women’s empowerment and youth skill-building to climate-resilient farming and natural resource management, every initiative we lead is grounded in community participation and built for long-term resilience.
Ongoing Projects
Online Marketing Initiative for Women SHG Weavers – Sironj
Empowering Rural Artisans Through E-Commerce & Digital Branding
Implemented by CIDA with support from NABARD, this initiative empowers 60 minority women weavers from 7 SHGs in Hajipur village, Sironj (Vidisha district) to transform their traditional handloom skills into digital micro-enterprises. Through branding, e-commerce onboarding, and digital storytelling, the women launched their own label—Sironj Weavers Collection—and connected directly with buyers online.
Key Highlights
- Digital Skills Training on social media marketing, pricing, and branding
- E-Commerce Onboarding via ONDC platform (MYSTORE)
- Brand Launch with logo, product catalogues, and packaging
- Market Access through exhibitions, social platforms, and media coverage
- ₹1 lakh+ in sales generated from direct buyer engagement
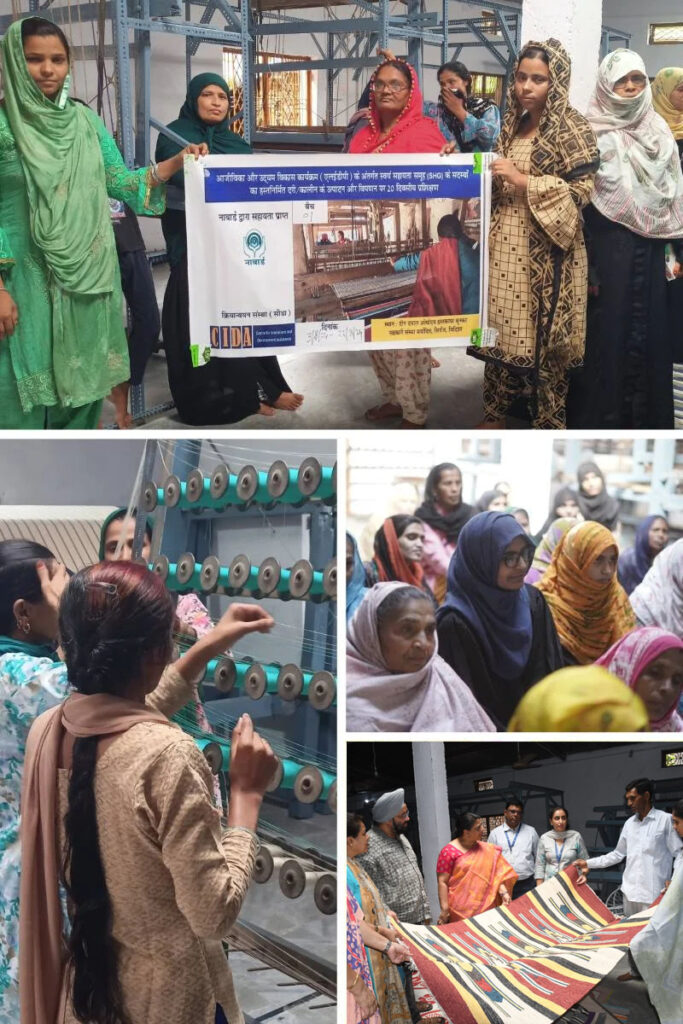

Livelihood and Enterprise Development Programme (LEDP)
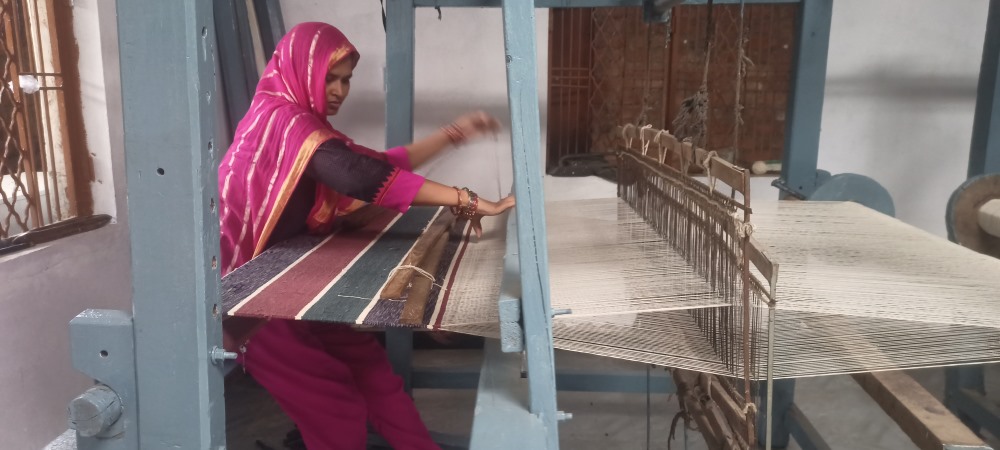
Implemented by CIDA with support from NABARD, this LEDP project empowers 60 minority women weavers in Hajipur village, Sironj block (Vidisha district), by reviving traditional durrie and rug weaving. The initiative focuses on skill enhancement, enterprise development, infrastructure support, and digital market access under the unified brand “Sironj Weavers Collection.”

Key Achievements:
Skill Training & Capacity Building
60 women from 7 SHGs trained in two 20-day batches. Covered traditional & modern techniques: warping, pile weaving, finishing, and design. Delivered by expert trainers at Deen Dayal Antyoday Hathkargha Bunkar Sanstha.
Marketing & Digital Empowerment
Workshop on branding, pricing, e-commerce, and digital storytelling. Training on platforms: WhatsApp Business, Facebook, Instagram, YouTube.
Exposure & Peer Learning
Exposure visit to Chanderi Handloom Cluster for best practices in cooperative models and innovation.
Infrastructure Strengthening
Renovation of Common Facility Centre (CFC) with new/refurbished looms, improved workspace.
Branding & Promotion
Launch of "Sironj Weavers Collection" with logo, catalogues, tags, and packaging. Product photoshoots and social media campaigns.
Market Access & Exhibitions
Participation in 5 major fairs including Gramin Utsav, Pari Bazar, PNB Fair, and more. Generated over ₹1 lakh in sales; gained significant media attention.
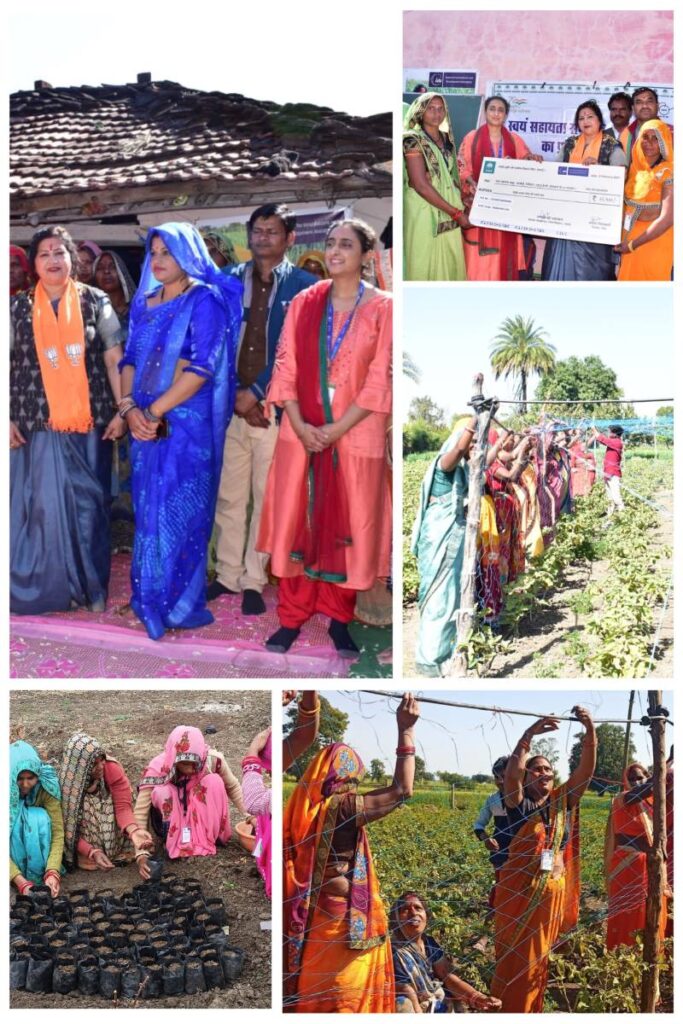
Micro Enterprise Development Programme (MEDP)
Building Agri-Entrepreneurship Skills for Rural Women
With the support from NABARD, this Micro Entrepreneurship Development Programme empowered 32 rural women from Self-Help Groups (SHGs) in Bhatkhedi, Vidisha to become agri-entrepreneurs. Provided hands-on training, participants learned how to turn small-scale vegetable farming into sustainable micro-enterprises.
The program focused on organic farming, business planning, and market readiness, helping women reduce input costs, improve crop quality, and build profitable farm-based ventures.
Key Outcomes
- Built agri-business skills among 32 SHG women
- Promoted organic, sustainable farming practices
- Enabled access to finance and market linkages
- Sparked the formation of women-led micro-enterprise groups
- Strengthened self-reliance and income security at the household level

Previous Projects
Farmer Producer Organisation (FPO) Development
To strengthen the agricultural economy and improve farmer incomes, CIDA facilitated the formation of 4 Farmer Producer Organisations (FPOs) and registered 4 Farmer Producer Cooperatives (FPCs) under the Cooperative Act in Chhattarpur and Gwalior districts, with financial support from Manthan Gramin Vikas Evam Samaj Sewa Samiti, Bhopal.
Each FPO engaged 300 smallholding farmers, supporting them in:
- Mobilizing share capital
- Accessing government schemes
- Building institutional capacities
- Establishing linkages with banks and markets
This initiative was aligned with the Government of India’s Central Sector Scheme to promote 10,000 FPOs for enhancing collective strength, better technology access, and improved market linkage for small and marginal farmers.
Enhancing Farm Productivity
CIDA trained over 150 smallholding farmers and 60+ women SHG members in Shahdol district to improve farm productivity through:
- Distribution of agricultural equipment and quality seeds
- On-field training for summer vegetable cultivation
- Seedling production techniques for crop sustainability
These interventions contributed to increased yields, better food security, and enhanced livelihoods for rural families.
Promoting Organic Practices in Agriculture
To reduce chemical dependency and improve soil health, CIDA promoted the use of organic manures and bio-fertilizers among smallholder farmers. Key efforts included:
- Adoption of Azolla and Vermi Compost by all 60 trained farmers
- Use of natural pesticides and composting techniques
- Improved awareness on food safety and environmental impact
This resulted in the production of high-quality, chemical-free vegetables for household consumption and local markets.
Low-Cost, Appropriate Farming Technologies
Recognizing the financial limitations of tribal and smallholder farmers, CIDA—in partnership with Abhivyakti Mahila and Bal Vikas Manch—promoted affordable and practical technologies in Jaisinghnagar and Budhar blocks of Shahdol. Activities included:
- Training 60 farmers on the use of vermi-wash, light traps, and organic inputs
- Distribution of materials such as seedling bags, plastic mulching sheets, and 1,400 banana seedlings
- Use of intercropping techniques and on-farm demonstrations
These efforts resulted in up to fivefold increases in household incomes and a shift toward more sustainable farming models.
Market Linkage & Value Chain Strengthening
CIDA supported farmer collectives and SHGs in marketing farm produce such as honey and spices through:
- Exhibiting products at Bhopal Haat in collaboration with Tribes India
- Promoting storytelling-based branding and local value chains
- Enabling access to online and offline sales channels
These activities helped small farmers secure better prices and recognition for their products.
Renewable Energy Promotion
In line with the National Solar Mission, CIDA promoted clean energy use among rural households by:
- Distributing solar lanterns to tribal families in remote areas
- Organizing solar awareness exhibitions at venues like Van Vihar, Bhopal
- Educating communities on the benefits of renewable energy solutions
This initiative improved access to lighting, reduced dependence on kerosene, and supported climate-resilient rural development.
Research Studies Conducted


















Research, Studies conducted
- Study on Various Aspects of Tendu Patta and Bidi including its Practices and Policies in the State of Madhya Pradesh – Madhya Pradesh Voluntary Health Association, 2021
- Conducted a Comparative Analysis of the Wage Structure for administrative and managerial cadre of all contractual employees under the National Health Mission (NHM) in Madhya Pradesh, comparing it with NHM Uttar Pradesh and Chhattisgarh – AIGGPA, 2021.
- Completed a Third-Party Monitoring and Impact Evaluation of Drip and Sprinkler Irrigation Assets under the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) across 26 districts and 2,098 farmers in Madhya Pradesh – NABCONS, 2021.
- Conducted a Process and Outcome Evaluation of Participatory Learning and Action (PLA), a community-based intervention to improve maternal and child health in Madhya Pradesh – AIGGPA 2021.
- Assessed contributing factors to the decline in child malnutrition and child mortality in Sheopur district, with a focus on childcare, capacity building, and awareness – Vikas Samvad, 2021
- Carried out a Study on the Lives and Livelihoods of Migrant Workers who returned home during the COVID-19 pandemic – AIGGPA 2020.
- Documented the process of transforming Anganwadi Centres into Bal Shiksha Kendras and scaling Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) in Madhya Pradesh – DWCD, 2020.
- Conducted an Analysis of Janani Express and 108 Emergency Medical Services in Madhya Pradesh – AIGGPA, 2020.
- Assessed the Optimum Rates for Manual Activities at procurement centres in Madhya Pradesh – AIGGPA, 2020.
- Conducted a Training Needs Assessment for 2,485 Sector Supervisors of the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) Mission – DWCD, 2014.
Documentary Film Produced
- Produced a documentary film on Anganwadi Workers’ Response to COVID-19 in Madhya Pradesh – 2021.
- Produced a promotional short film on COVID-19 – An Appeal from all to take vaccine and maintain health and hygiene – Madhya Pradesh Voluntary Health Association, 2021
- Produced a documentary film on how people with disabilities managed their lives during the COVID-19 pandemic across six states in Sightsavers’ programme areas – 2021.
- Produced “Divyam”, a documentary film on the Inclusive Education Programme for People with Disabilities in Madhya Pradesh – 2021, for Sightsavers International, India.
- Produced “Swavlamban”, a documentary film on the Social Inclusion Programme for People with Disabilities in Madhya Pradesh – 2021, for Sightsavers International, India.
- Produced “Breaking Barriers”, a documentary film on the Social Inclusion Programme for People with Disabilities in Rajasthan – 2021, for Sightsavers International, India.
High Quality Reports produced
- Consensus Study Report on Composition of Policies and Legislation Banning Smokeless Tobacco / Gutkha in India, Madhya Pradesh Voluntary Health Association, 2022
- Produced a report on Estimating Early Neonatal, Post-Neonatal, and Infant Mortality through Live Birth and Infant Death Tracking System – AIGGPA, 2020.
- Produced the Child Protection Week – Madhya Pradesh State Campaign Report – Department for Women and Child Development, Government of Madhya Pradesh, 2020.
- Produced the Beti Bachao Beti Padhao – Madhya Pradesh State Campaign Report – Department for Women and Child Development, Government of Madhya Pradesh, 2020.
- Documented Response to COVID-19: Stories of Inspirational Successes and Unparalleled Heroism of Anganwadi Workers in Madhya Pradesh – Department for Women and Child Development, Government of Madhya Pradesh, 2020.
- Produced the World Breastfeeding Week Report – 2019 Department for Women and Child Development, Government of Madhya Pradesh.
- Conducted a Growth Monitoring and Promotion (GMP) Analysis comparing month-wise data for children aged 0–5 years across 13 districts in Madhya Pradesh – Department for Women and Child Development, Government of Madhya Pradesh 2014.
- Developed a Participatory Monitoring, Supervision, Evaluation, and Research Manual for the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) Mission – 2014.
- Produced the Anganwadi Centres (306) Assessment Report for the Department for Women and Child Development (DWCD), ICDS Mission – 2014.
- Produced the World Breastfeeding Week Report – 2014, Department for Women and Child Development, Government of Madhya Pradesh.
- Produced the World Breastfeeding Week Report – 2013 Department for Women and Child Development, Government of Madhya Pradesh.